
Scientists have discovered 'dark' genes in our DNA that have been majorly overlooked until now.
For years, researchers thought certain regions of DNA didn't do much, labelling them as 'junk DNA.'
Therefore, our records of the human genome, discovered 20 years ago, are probably missing maybe tens of thousands of 'dark' genes.
But it turns out that some of these areas hold instructions for creating tiny proteins. They are now being linked to important biological processes like cancer and immunology, a global consortium of researchers has confirmed.
Advert
The new international study, still awaiting peer review, shows our library of human genes very much continues to be a work in progress, as more subtle genetic features are picked up with advances in technology, and as continued exploration uncovers gaps and errors in the record.
Institute of Systems Biology proteomicist Eric Deutsch and colleagues dug into genetic data from 95,520 experiments for fragments of protein-coding sequence. They used mass spectrometry to investigate small proteins and examined catalogues of protein fragments identified by our immune systems.

Unlike traditional genes with long, recognisable starting codes, these 'dark' genes have much shorter starting sequences, making them easier to miss.
The non-canonical open reading frame (ncORF) genes are still used as a template to create RNA and some of those are then used to make small proteins, despite their incomplete start sequences.
"We believe the identification of these newly-confirmed ncORF proteins is immensely important," the team wrote in their paper.
"Their proteins[…] may have direct biomedical relevance, which is manifested in the growing interest in targeting such cryptic peptides with cancer immunotherapy, including cellular therapies and therapeutic vaccines."
Some of the genes responsible for these cryptic peptides come from transposons - DNA elements that move around the genome, including bits left behind by viruses.
Other parts are what the researchers refer to as 'aberrant' which means they only exist in certain circumstances. For instance, some proteins identified through mass spectrometry have only been found in cancer samples which suggests that their associated genes might not naturally belong in the body.
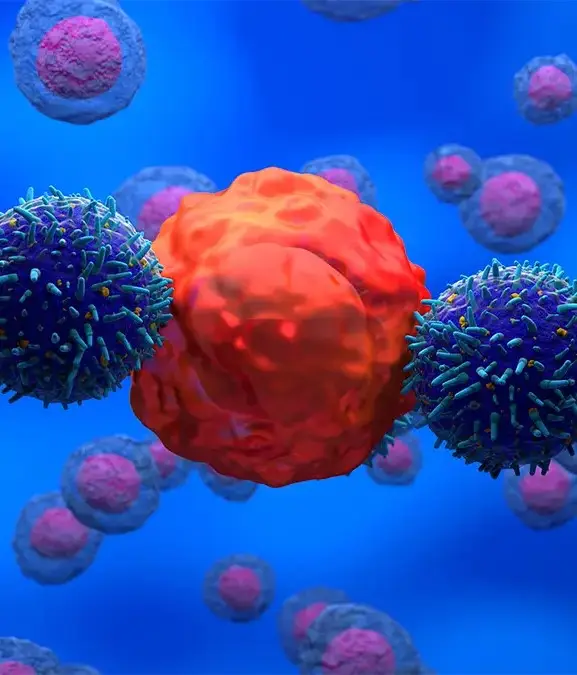
"Thus, it remains possible that certain ncORF peptides reflect aberrant proteins whose existence is deemed out of context with the canonical proteome," Deutsch and his team explained.
Out of 7,264 sets of these non-canonical genes, the researchers discovered that at least a quarter of them could produce proteins.
This amounted to at least 3,000 new peptide-coding genes that can now be added to the Human Genome. This could mean wonders for the tens of thousands more that have all been overlooked by previous proteomic techniques.
"It's not every day that you get to open a research direction and say, 'We might have a whole new class of drug targets for patients,'" said University of Michigan neurooncologist John Prensner.
The tools developed during this study will help scientists continue to explore this dark side of our DNA. And maybe one day we can fill the gaps we have about our current genome.